Habitualization 101: How to Create and Maintain Habits Effortlessly
Dec 7, 2023
By Will Moore
Imagine that you could achieve any goal you set for yourself, whether it’s learning a new skill, losing weight, or starting a business. How would that change your life? What if I told you that there is a simple and proven way to make this happen and that it all comes down to one thing: habitualization.
So, let’s learn how to master habitualization and transform your actions into lasting habits in all 5 pillars of life.
Life Upgrades You'll Receive
Understanding Habitualization: Learn how turning actions into automatic habits can help achieve personal goals.
Psychology of Habits: Understand the habit loop (cue, routine, reward) and its role in forming lasting habits.
Life Impact: Explore how habitual behaviors shape daily life, relationships, and society.
Practical Guide: Step-by-step strategies for creating habits in key life areas: Mind, Body, Relationships, Career, and Finances.
Sustaining Habits: Tips on making habits stick for long-term identity and behavior change.
What is Habitualization?
Simply put, habitualization is the process of turning your actions into habits, so that they become automatic and effortless. A habit is a pattern of behavior that you repeat regularly and subconsciously, without having to think about it or motivate yourself to do it. For example, brushing your teeth, checking your phone, following a morning routine checklist, or driving to work are all habits that you perform in everyday life without much conscious effort.
How Habitualization works? The Psychology Behind.
Habits form and stick because of a psychological mechanism called the habit loop. The habit loop consists of three components: a cue, a routine, and a reward.
A cue is a trigger that initiates the habit, such as a time of day, a location, or an emotion. A routine is the action you perform in response to the cue, such as eating, exercising, or smoking. A reward is the benefit you get from the routine, such as pleasure, satisfaction, or relief.
The habit loop works like this: when you encounter a cue, your brain associates it with a routine and a reward and creates a craving for the reward. This craving motivates you to perform the routine, which then delivers the reward and reinforces the habit. The more you repeat the cue-reward cycle, the stronger the habit becomes, until it becomes part of your identity and behavior. This is how habitualization works.
How do Habitual Behaviors Shape Our Lives?
Habitualization is not only a psychological phenomenon but also a practical one. It affects how we live our daily lives, from the moment we wake up to the moment we go to sleep. Here are some examples of how habitual behaviors shape our lives:

We frequently follow a morning routine, such as brushing our teeth, taking a shower, having breakfast, and getting ready for work or school. These habits help us start our day with a sense of order and efficiency.
We often rely on habits to perform complex tasks, such as driving, typing, or playing an instrument. These habits allow us to execute these skills with ease and accuracy, without having to think about every step or movement.
We sometimes use habits to cope with stress, boredom, or negative emotions, such as smoking, drinking, eating, or scrolling through social media. These habits provide us with temporary dopamine, but they may also have harmful consequences for our health and well-being.
The Ripple Effect of Habitual Behaviors
Habitual behaviors affect us not only individually but also collectively. They have a ripple effect that influences our society and our social interactions. As Berger and Luckmann said in the book Social Construction of Reality, “Identity is a phenomenon that emerges from the dialectic between individual and society.” This means that our habits reflect who we are and what we value they help us grow or hold us back, in both our personal and social domains.
Here’s how
Our habits shape our culture and our values, such as what we eat, what we wear, what we celebrate, and what we believe. These habits reflect our identity and heritage and may create stereotypes and biases.
Our habits affect our environment and our resources, such as how we consume, how we travel, how we dispose, and how we conserve. These habits determine our ecological footprint and sustainability but may also cause pollution and depletion.
Our habits influence our relationships and our communication, such as how we greet, how we listen, how we express, and how we connect. These habits foster our social skills and our empathy, but they may also lead to misunderstandings and conflicts.
Building New Behaviors – A Step-by-Step Guide to Habitualization
Habitualization is not a one-time event, but a continuous process. It is not enough to perform an action once or twice, or even for a few weeks. To truly transform an action into a habit, we need to make it a part of who we are and how we live.
The 5 cores of life are the main areas of happiness and fulfillment that we need to balance and improve, namely: Mind, Body, Relationships, Career, and Finances. Each core has its own set of habits that can either help us grow or hold us back.
Read More: How Long Does it Take to Build a Habit
For example, let’s say you want to improve your mind core by learning a new language. You have identified that your main failure habit is procrastinating and giving up on your language lessons. To replace this with a healthy habit, here are some steps you can take:
Make your actions consistent with your identity and values.
Think of yourself as a curious and adventurous person who loves to explore new cultures and communicate with different people. Remind yourself that learning a new language is in line with who you are and what you stand for.
1. Connect your action to your purpose and vision.
Have a clear and compelling reason for learning a new language and a vivid and inspiring picture of what you want to achieve and how you want to feel. For example, you may want to learn a new language to travel to your dream destination, to make new friends, or to advance your career.
2 .Adapt your action to your environment and context.
For example, set up a dedicated space for your language lessons, find a language partner or a tutor, or join a language learning community.
3. Gamify your action and make it fun and rewarding.
Use behavioral science and gamification techniques to trick your brain into wanting to learn a new language and making it so obvious, easy, fun, satisfying, and rewarding that you can’t help but do it. Use a weekly habit tracking app to review your language habits each morning and score yourself at night, using points, rewards, competition, and social connectivity to motivate and challenge yourself. Make the process of language learning fun and engaging.
From Action to Habit: Making It Stick
Creating a new habit is only the first step. The next step is to make it stick so that it becomes part of your identity and behavior. Here are some strategies to help you maintain your habit for the long term:
Repeat your habit regularly and consistently: The more you practice your habit, the more it becomes ingrained in your brain and your muscle memory. Aim for at least 60 days of continuous repetition, which is the minimum time needed to form a habit, according to some studies.
Use Habit Stacking: Habit stacking is a technique that can help you create and maintain new habits more easily. It involves adding a new habit to an existing one so that it forms a sequence or a routine.
For example, if you want to start meditating every morning, you can stack it with your habit of brushing your teeth. This way, you can use the cue of brushing your teeth to trigger your new habit of meditating.
Keep a record of your habit performance: Use a habit journal, a calendar, or an app. Review your habit periodically and evaluate your results. What are you doing well? What can you improve? How can you adjust your habits to suit your needs and preferences? Gamify every step to stay motivated.
Seek support and feedback. Find someone such as a friend, a family member, a coach, or a mentor. Share your goal and your plan with them, and ask them to hold you accountable, encourage you, and give you constructive feedback.
Be flexible and adaptable. Don’t be a perfectionist. Expect some setbacks and challenges, and don’t let them discourage you. Learn from your failures, and use them as opportunities to grow.
Why Habitualization is Key to Changing Behaviors
Habitualization is key to changing behaviors because it helps us:
Break free from the cycle of procrastination, resistance, and self-sabotage that prevents us from taking action and achieving our goals.
Replace our destructive habits with success habits.
Automate our desired behaviors, so that we don’t have to rely on willpower, motivation, or discipline, which are limited and unreliable resources.
Create a lasting and sustainable change, so that we don’t fall back into our old patterns and habits.
Personal Growth Through Habitualization – Strategies and Benefits
Habitualization is not only a way to change our behaviors, but also a way to improve and live a balanced life. Habitualization can help us achieve our personal goals and fulfill our potential, but it requires consistent and deliberate effort.
Here are some practical tips and benefits of using habitualization for self-improvement:
Choose habits that align with your strengths, passions, and interests. This will make your habits more enjoyable and meaningful, and increase your motivation and engagement.
Choose habits that challenge you and push you out of your comfort zone. This will make your habits more stimulating and rewarding, and increase your learning and growth.
Choose habits that complement and reinforce each other. This will make your habits more synergistic and effective, and increase your performance and results.
Choose habits that balance and harmonize your 5 cores of life. This will make your habits more holistic and sustainable, and increase your well-being and happiness.
Evolving Through Habits
Habitualization is not a one-time event, but a continuous process. It is not enough to create and maintain habits, we also need to evolve and update them. Habits are the building blocks of our evolution, and our evolution determines our destiny. By evolving our habits, we can evolve ourselves, and by evolving ourselves, we can evolve our world.
How Can You Use Habitualization to Change Your Equation of Life and Level Up Your Happiness?
The equation of life is a formula that shows how your belief system, your repeated actions, and time determine who you will become. By changing any of these variables, you can change your equation and your destiny.
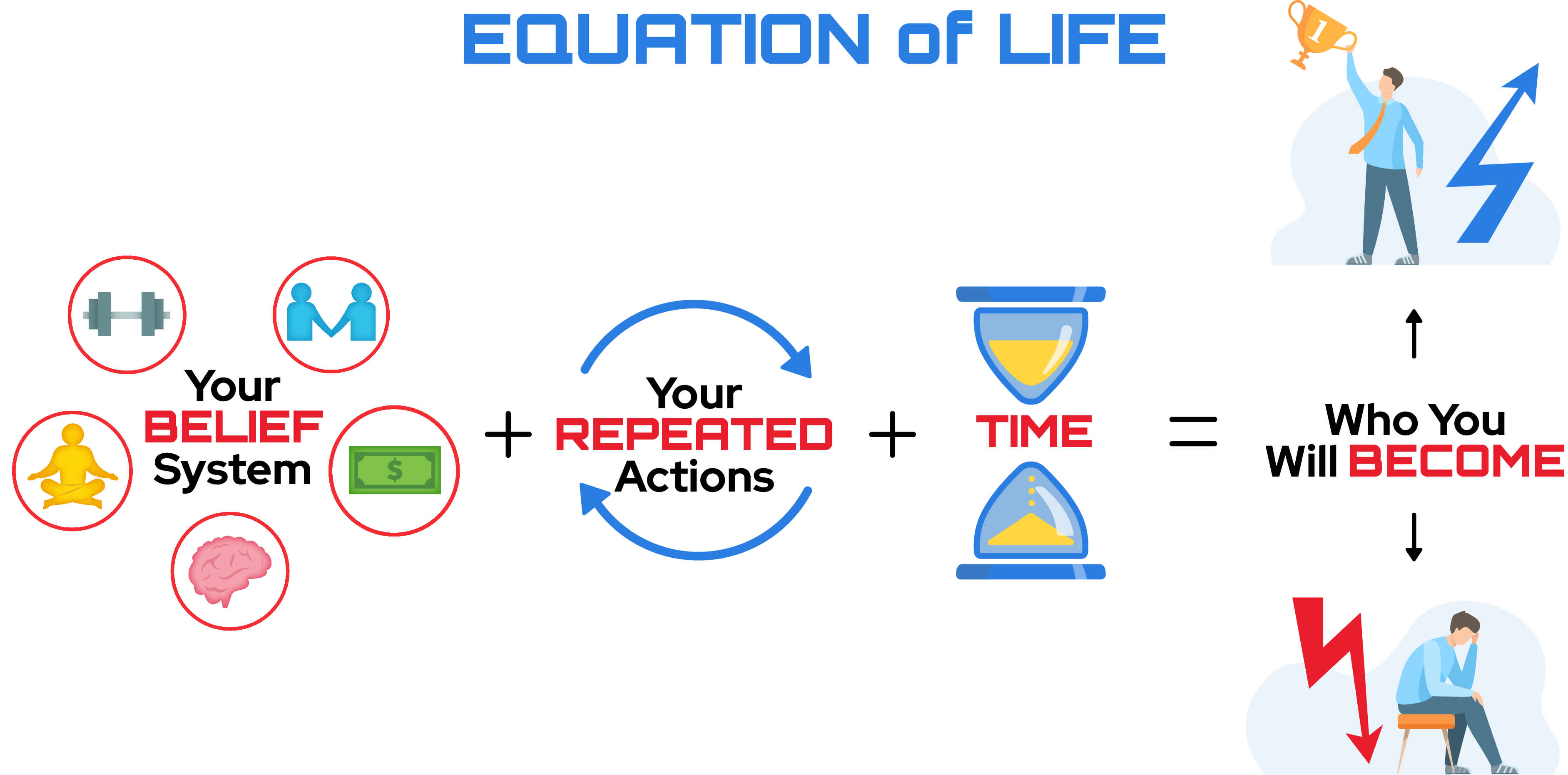
Imagine that your life is a video game, and you are the main character. Your belief system is the set of rules and objectives that guide your gameplay. Your repeated actions are the moves and skills you use to play the game. Time is the level and the score that you achieve in the game.
Check our Podcast on Mindfulness and Meditation
Now by using this equation, you can master habitualization and create and maintain habits that align with your 5 cores of life and your personal goals.
Ready to Transform Your Life?
Habitualization can make your life better, but you need to apply what you learned. This article was a step into a world where your dreams are possible. This is where the fun starts!
You learned strategies and insights from proven methods that use behavioral science, gamification, technology, and universal principles. These methods can help you improve your 5 Core Areas: Mindset, Career & Finances, Relationships, Physical Health, and Emotional & Mental Health
🚀🚀���🚀 To start this amazing journey, you need to find out how your current habits affect these vital areas of your life. Take our quick, 2-minute “Core Values Quiz”
By using the MM system, you can gamify the process of habitualization and make it fun and rewarding.
FAQS
What is an example of habitualization?
Habitualization is when we do something so often that it becomes a habit and we don’t think much about it. For example, brushing our teeth every morning is a habit we do automatically.
What is the difference between habitualization and institutionalization?
Habitualization is when our actions become patterns that we repeat easily and frequently. Institutionalization is when these patterns become part of society and are accepted as norms and rules. For example, driving on the right side of the road in the US is a habit that has become an institution with traffic laws.
How does habitualization affect our perception of reality?
Habitualization makes us take our daily habits and patterns for granted and not question them. This can limit our creativity and openness to change. It can also make us expect others to follow the same habits as we do.
How can we overcome habitualization?
We can overcome habitualization by being more aware and critical of our own habits and the social structures that shape them. We can also try new things, learn new things, or see things from different perspectives. This can help us create our own reality.
